Designing Greener Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Insights from the pharmaceutical industry into drug discovery and development
- Publication
- Citation
Puhlmann, N., Vidaurre, R. and Kümmerer, K. (2024) ‘Designing Greener Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: Insights from pharmaceutical industry into drug discovery and development’, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 192, p. 106614. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106614.
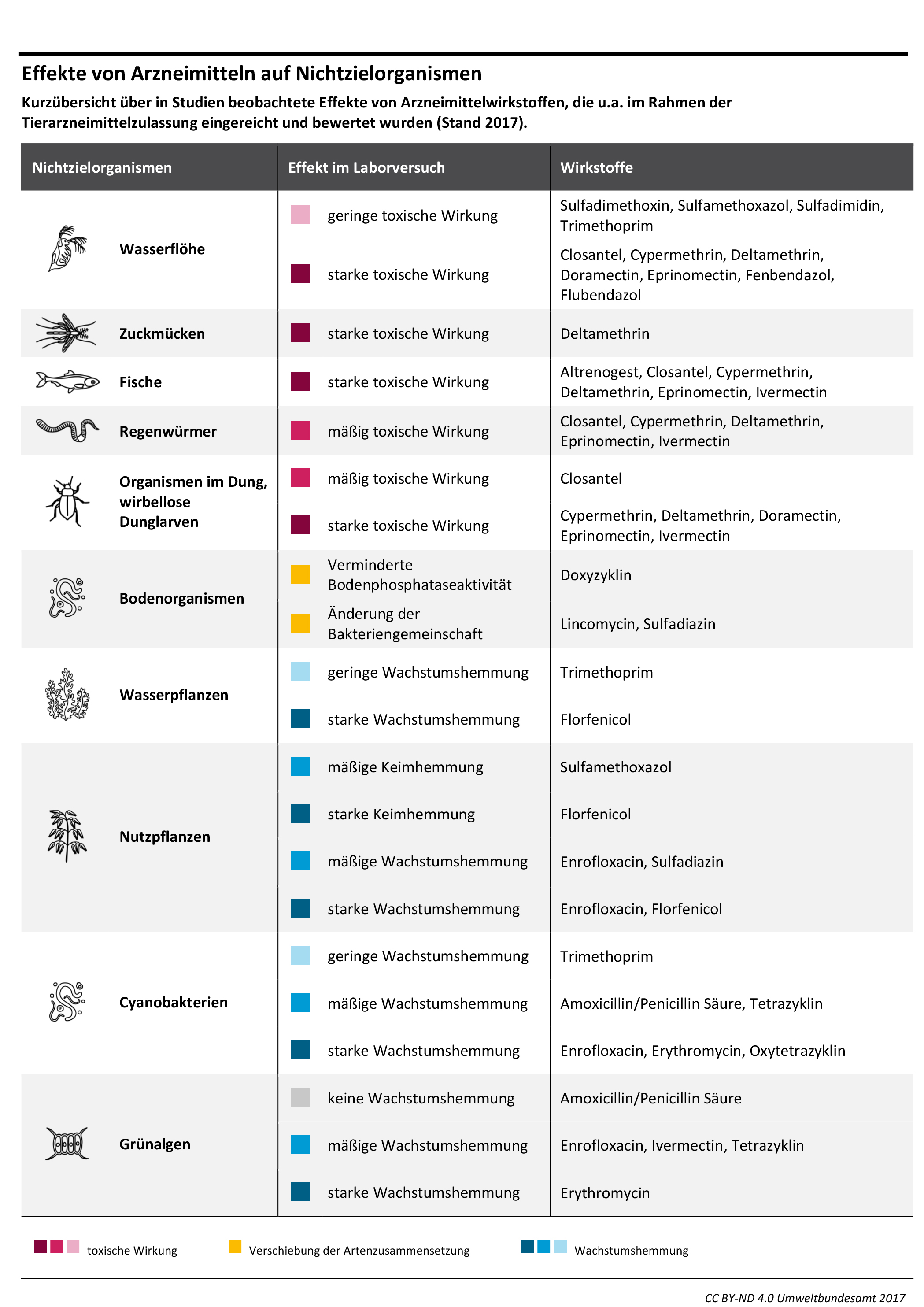
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), their metabolites, and transformation products often act as pollutants in the environment, impacting both ecosystems and human health. To tackle this issue, an efficient, long-term prevention strategy involves designing APIs with reduced environmental impact – i.e. 'greener' APIs. This involves incorporating environmental parameters into the pharmaceutical Research and Development (R&D) process. This article explores the feasibility of designing greener APIs, drawing insights from drug design experts in major research-based pharmaceutical companies. The feasibility assessment identifies needs and incentives for process modification, based on interviews with 30 R&D and environmental experts from seven globally active pharmaceutical companies.
Opportunities and Challenges in API Design
Key findings indicate that experts see numerous opportunities to integrate environmentally friendly properties at various stages of the R&D process. The flexibility of the pharmaceutical R&D process, which relies on balancing multiple parameters, can facilitate this integration. Additionally, certain API properties that reduce environmental risks align with common desirable application properties.
Early Integration of Environmental Aspects in the R&D Process
Environmental considerations should be incorporated early in the R&D process, during molecule screening and optimization. Availability of suitable in silico models and in vitro assays is crucial for this, with attributes such as throughput and costs determining their successful application at different process stages.
Collaboration for Sustainable Innovation
Enhanced collaboration between R&D and environmental experts, both within and outside companies, can advance the industrial application of the benign-by-design approach for APIs. Collaborative efforts spanning pharmaceutical companies, regulatory authorities, and academia are deemed highly promising. Financial, social, and regulatory incentives would further support the future design of greener APIs.